cca_robotics_2021
Course materials for CCA high-school robotics class, academic year 2021-22.
Project maintained by buffetboy2001 Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Sense an Obstacle
Module Goal: connect your obstacle sensor and write Python code to use it!
Acknowledgement: images and python code snippets in this module are copied directly from the this excellent PiHut tutorial.
What You Need
- 8 wires (select four unique colors, if possible)
- the obstacle sensor
- two resistors (ask Mr. Bowman)
- the breadboard
Assembly
Examine the obstacle sensor’s four connections. It looks like this:
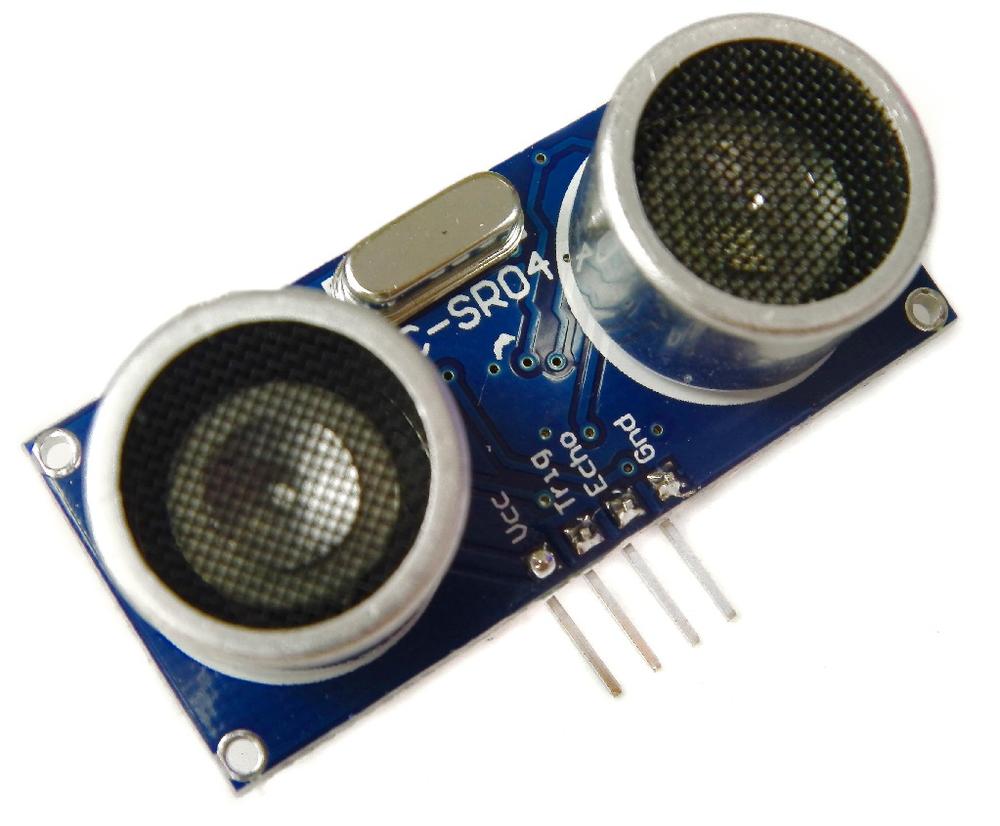

Connect these wires:
- Connect the VCC wire to pin 2 on the Raspberry Pi
- Connect the TRIG wire to pin 23 on the Raspberry Pi
Now for the breadboard connections. First, add your resistors like this:
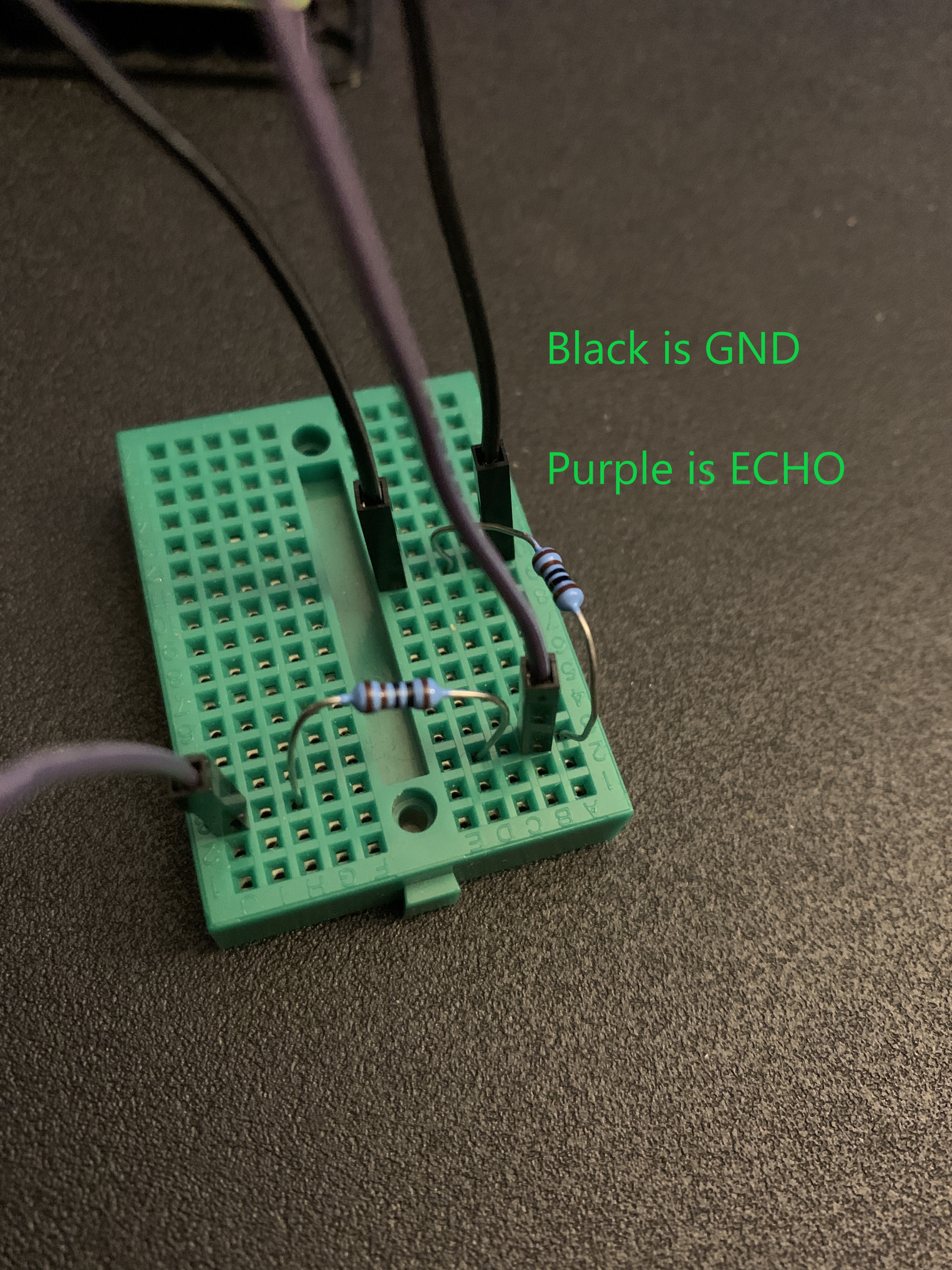
Next:
- Connect the GND wire to any GND on the Raspberry Pi
- connect the other end to the breadboared like in the picture
- Connect the ECHO wire to pin 24 on the Raspberry Pi
- connect the other end to the breadboard like in the picture
This sensor can only work with some code to interpret the signals.
Python Code
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
#GPIO Mode (BOARD / BCM)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
#set GPIO Pins
GPIO_TRIGGER = 23
GPIO_ECHO = 24
#set GPIO direction (IN / OUT)
GPIO.setup(GPIO_TRIGGER, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(GPIO_ECHO, GPIO.IN)
def distance():
# set Trigger to LOW, then HIGH
GPIO.output(GPIO_TRIGGER, False)
time.sleep(1)
GPIO.output(GPIO_TRIGGER, True)
# set Trigger after 0.01ms to LOW
time.sleep(0.00001)
GPIO.output(GPIO_TRIGGER, False)
StartTime = time.time()
print(f'StartTime:{StartTime}')
StopTime = time.time()
print(f'StopTime:{StopTime}')
# save StartTime
while GPIO.input(GPIO_ECHO) == 0:
pass
StartTime = time.time()
# save time of arrival
print('looking for low while high')
while GPIO.input(GPIO_ECHO) == 1:
pass
StopTime = time.time()
print('echo went low and exited')
# time difference between start and arrival
TimeElapsed = StopTime - StartTime
# multiply with the sonic speed (34300 cm/s)
# and divide by 2, because there and back
distance = (TimeElapsed * 34300) / 2
return distance
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
dist = distance()
print ("Measured Distance = %.1f cm" % dist)
time.sleep(1)
# Reset by pressing CTRL + C
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Measurement stopped by User")
GPIO.cleanup()
Try It Out
Place your sensor directly in front of a solid object that is close-by (1 foot away). Run the script and observe the output.
Hopefully, you’ve got sensor readings telling you how far away (approximately) the object is.
Module Complete